Prosthodontist vs Endodontist. Let’s Break It Down:
June 7, 2021
How to Select an Endodontist
July 7, 2021
Prosthodontist vs Endodontist. Let’s Break It Down:
June 7, 2021
How to Select an Endodontist
July 7, 2021During endodontic procedures, the doctor may use equipment that seems foreign to the patient. Because at Innovative Endodontics we want to help our patients to feel comfortable throughout their procedures, therefore we offer education in addition to our services. Consequently, we have this guide covering a common question that we get from our patients during root canal therapies, “What is a dental dam in dentistry?”
What Is a Dental Dam in Dentistry?
The dental dam, also known as a rubber dam, is a piece of latex or non-latex material in a square shape that fits over the mouth. These pieces have a hole in the center to accommodate one or multiple teeth for the required procedure. Because some dental dams use latex, patients with known latex allergies need to inform their endodontist or dentist about the allergy. The doctor can use a non-latex dental dam for the patient to prevent a reaction.
A dental dam for dental procedures provides a means of protection and safety for the patient. It serves as an added safety feature to remove infections and prevents complications from any type of dental procedure.
A dental dam in dentistry fits around the tooth the endodontist works on for non-surgical root canal treatment. Dentists may also use these when filling cavities, placing veneers, or fitting crowns on teeth. When dental professionals use dental dams, both the patient and practitioner benefit.
How Do Endodontists Use Dental Dams?
Endodontists use dental dams as a standard of care. In fact, the American Association of Endodontists supports the use of this piece of equipment for all non-surgical endodontic treatments, including endodontic retreatment and root canal therapy.
Before non-surgical endodontic treatment, the doctor will prepare the area in various ways. First, they will numb the area with a local anesthesia to the gum. Next, they must isolate the tooth that requires treatment with a dental dam. They fit the dam around the tooth by placing the tooth through the hole. The dental dam is gently held in place with something called a clamp, which hugs around the tooth and then it gently stretches over the mouth.
The dental dam is gently held in place with something called a clamp which hugs around the tooth and then it gently stretches over the mouth. Your endodontist will be happy to show you this safety measure and explain its components and steps for placement.
You may see the dental dams used by endodontists in different colors. Practitioners have the option of choosing the colors that they prefer. Light-colored dental dams reflect light to the area. However, darker dams make it easier for the tooth itself to stand out against the dental dam. Color options depend on what the endodontist feels best serves their efforts.
After finishing the procedure, the endodontist will remove the clamp to gently remove the dam from the tooth. They will also take the frame off the mouth to take the rest of the dam away. After use, they discard the dental dam because it is a single-use item.
Benefits of a Dental Dam in Dentistry and Endodontics
A dental dam helps patients and endodontists during non-surgical care. By isolating the tooth during the procedure, the endodontist can avoid harm and protect the patient. The benefits for both individuals mean better treatment, more comfort, and greater protection. Overall, the patient gets better care, and the endodontist can improve their treatment.
Endodontists Protect Themselves from Aerosols
First, a dental dam offers protection for the endodontist. Blocking off the rest of the mouth prevents the aerosols from touching the doctor. The dam blocks off access to these body fluids by isolating the tooth and keeping the rest of the mouth closed off.
This reduction of aerosols has also been incredibly important during the COVID-19 pandemic and the American Dental Association has strongly emphasized its use in dentistry to reduce the spread during dental treatment.
Endodontists Improve Treatment
Care for the patient’s tooth improves when the endodontist isolates the area. They can more easily focus only on the treated tooth. Plus, the type of dam coloring can improve lighting in the area or provide adequate contrast to see the tooth better. With a dental dam, the doctor can treat the patient better, which improves the experience both have during the procedure.
Site Protection and Isolation
Isolating the tooth from the rest of the mouth also protects the patient. Saliva cannot get into the tooth, where it could cause a later infection. Plus, by blocking off other mouth tissues, the endodontist minimizes the chances of accidentally injuring part of the patient’s mouth during the procedure.
The rest of the patient’s mouth also has a barrier against dental tools, tissue, blood, pulp, or tooth pieces. Preventing these foreign objects from getting into the mouth and accidentally being swallowed provides another added layer of protection for the patient.
Other Safety Measures Endodontists Use to Protect Patients
Endodontists don’t use only dental dams to protect their patients. They also use other measures to keep patients safe and comfortable. These measures include communication, education, and technology to ease fears and provide more precise endodontic care.
Communication is vital to a successful and comfortable patient experience. Whenever a patient has concerns in the chair during a procedure, they only have to raise their hand for the endodontist to stop and discuss what the patient needs.
Reducing fear by explaining procedures and equipment is also important. The majority of dental anxiety and apprehension is because most patients do not know what to expect during treatment. A good endodontist will explain the steps as they occur and will guide you through the entire treatment.
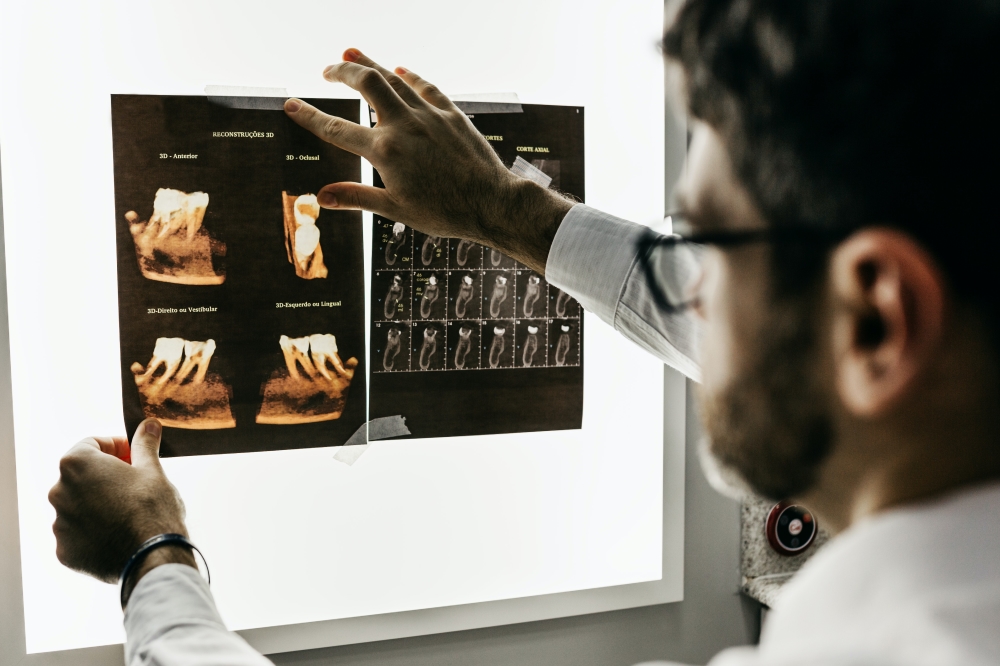
Precise planning through imaging of the area before either a non-surgical or surgical procedure also ensures that the endodontist needs to conduct minimal physical exploration to identify the area for treatment and properly remove the infected matter.
Contact Innovative Endodontics for Care That Puts Our Patients’ Safety and Comfort First
Our patient’s comfort and safety come first at Innovative Endodontics. So, when you need endodontic care in North Charleston, SC, or the surrounding areas, contact us for an appointment. We pride ourselves on exceeding standard care to improve our patient’s experience and fulfill our motto of changing the reputation of the root canal. Hope you got an answer to what is a Dental Dam.